The
Boomerang Nebula is a young planetary nebula and the coldest object found in the Universe so far. The
NASA/
ESA Hubble Space Telescope image is yet another example of how Hubble's sharp eye reveals surprising details in celestial objects.(...)With a temperature of -272C, it is only 1 degree warmer than absolute zero (the lowest limit for all temperatures). Even the -270C background glow from the Big Bang is warmer than this nebula. It is the only object found so far that has a temperature lower than the background radiation.
View: https://www.spacetelescope.org/images/heic0301a/
https://cdn.spacetelescope.org/archives/images/thumb700x/heic0301a.jpg
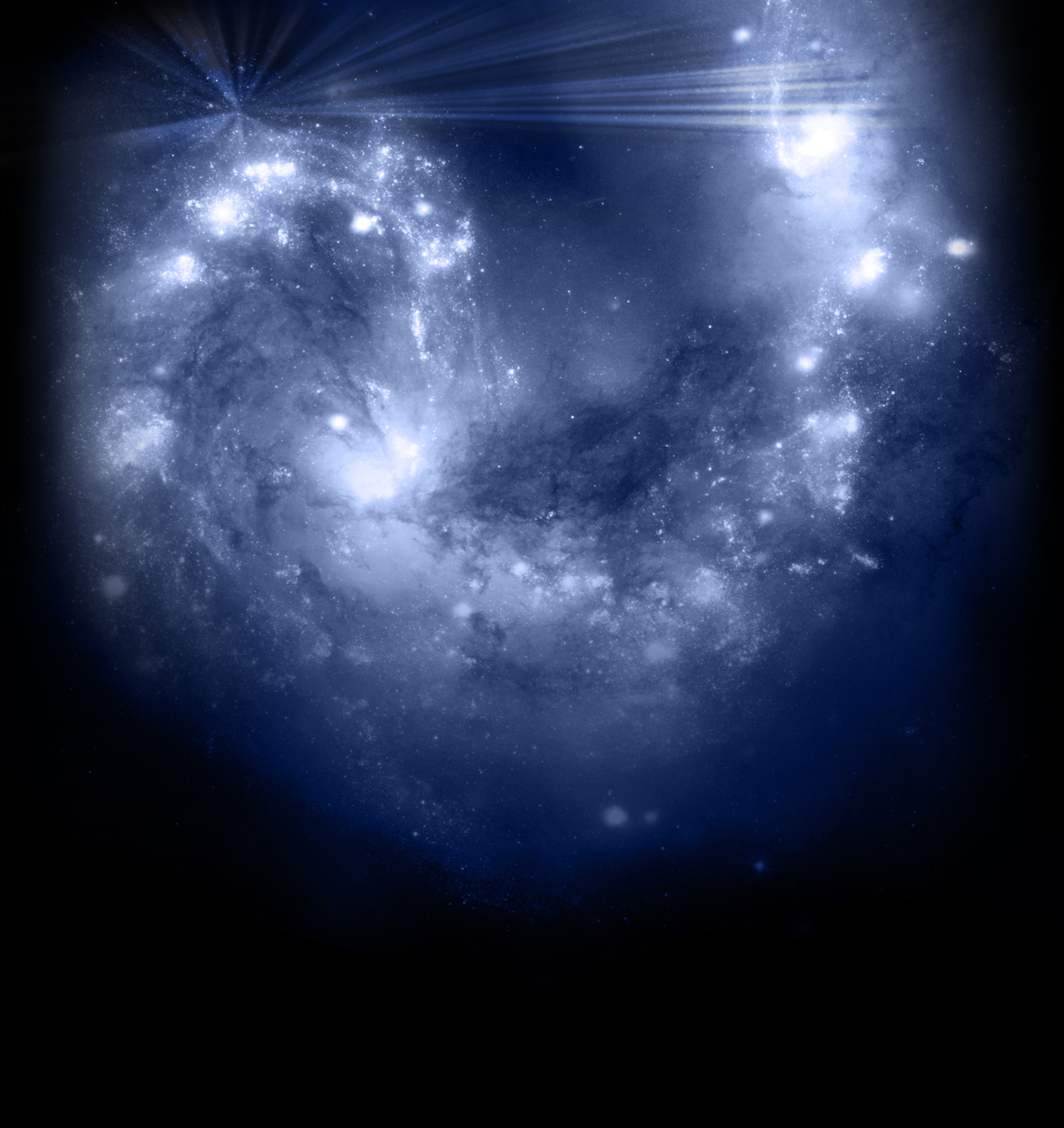
Magellanic Cloud: The tip of the "wing" of the Small Magellanic Cloud galaxy is dazzling in this new view from NASA's Great Observatories. The Small Magellanic Cloud, or SMC, is a small galaxy about 200,000 light-years way that orbits our own Milky Way spiral galaxy.
http://www.nasa.gov/images/content/738996main_pia16884-43_946-710.jpg
(...)The SMC is one of the Milky Way's closest galactic neighbors. Even though it is a small, or so-called dwarf galaxy, the SMC is so bright that it is visible to the unaided eye from the Southern Hemisphere and near the equator. Many navigators, including Ferdinand Magellan who lends his name to the SMC, used it to help find their way across the oceans.(...)
View: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/spitzer/multimedia/pia16884.html